Passive House
(Passivhaus)
Passive House or “Passivhaus”(German) is an internationally recognized building standard developed through the Passivhaus Institute based in Darmstadt, Germany. Passive House Principles apply to all building types, not just houses. The “haus” translates to “building” in German.
Passive House is an envelope first approach. By using Passive house principles & design tools, we can create durable buildings that reduce heating/cooling energy use by up to 90%. All while creating quiet, comfortable, healthy homes with continuous filtered fresh air.
Think of it like this: Passive House is your “YETI” mug
Code minimum or older building
Passive House Building
Principles & Benefits
Continous insulation keeps the inside of your building warm in the winter and cool in the summer. Keeping occupants comfortable and eliminating the risk of condensation
Windows & Doors: When it comes to a high performing envelope, your wall is only as good as your weakest link. Every part of your envelope needs to work as a unit to achieve performance. Triple pane glazing with thermally broken/insulated frames keep interior surface temperatures warm. Creating comfortable, draft free environments & eliminating condensation on interior surfaces. Passive house certified windows can outperform conventional windows by 2-3x.
Orienation & Form: Passive house buildings can be any shape or form imaginable. Simpler building forms will lead to less jigs and jogs which in turn add surface area and heat loss. When the site permits, we orientate our building to the best views and best daylighting/solar access.
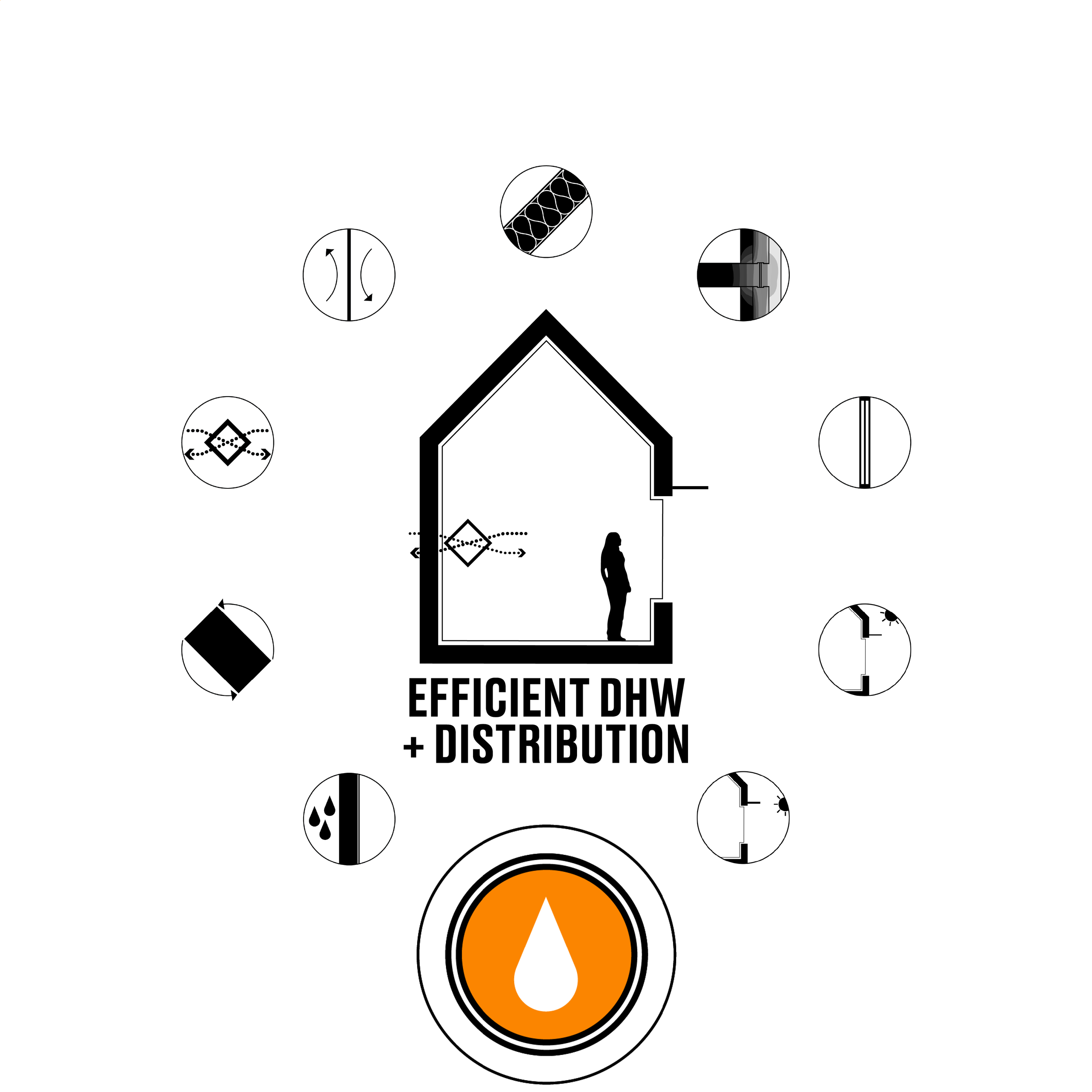
Efficient DHW + Distribution: When we dramatically reduce our heating demand, domestic hot water becomes a larger part of the energy use equation. By using efficient water heaters and laying out plumbing in a strategical way, energy consumption can be further optimized.
A Thermal bridge is an element that disrupts the thermal barrier, leading to heat loss and a fluctuation in interior surface temperatures. This can add up to big heat losses and potential risk for cold spot and mold growth on interior surfaces of your walls. Careful detailing is required to elimate or minimize thermal bridges.
Fresh air is provided to the building via HRV/ERVs (heat/energy recovery ventilators). These systems provide continuous filtered fresh air, while simultaneously extracting stale air. When extracting stale air HRV/ERVs retain up to 90% of your buildings heat. ERV’s can retain moisture in certain climates where that may be necessary. These systems work extremely well with a tight envelope, creating healthy indoor environments. Leading to healthy & happy occupants.
Glazing(daylighting) provides us with natural daylight as well as free solar heat gains. By strategically orienting glazing we can optimize the heat gains vs the heat losses in our buildings.
Air Tight: leakage = energy lost. By simply increasing building airtightness, we dramatically improve energy efficiency. Using membranes and building elements, a continuous air control layer is established. This keeps warm air in and cold air out. Reducing uncomfortable drafts and minimizing the risk of moisture intrusion/extrusion into building cavities.
Shading: During the winter months, properly orientated windows bring in free heat gains through low angle sun. In the summer, when the sun is at a higher angle, we want to provide proper shading to avoid overheating. This can be done with deciduous trees, roof overhangs, roller shades and more. Without affecting natural daylight.
Moisture Management: Controlling moisture is a key component in the longevity of buildings. By properly detailing the building enclosure, we can ensure strong building assemblies. Preventing bulk water such as rain from entering our buildings and proper membranes/components which will prevent vapour transfer and condensation.
Powerful Design & Optimization Software
As a Passive House Designer, we use the PHPP software to perform building physics calculations & energy modelling. Supplemental software is also used to calculate thermal bridge and other design details to predict actual real life performance numbers.
Infographics provided by the ‘Passive House Accelerator’. For more Passive house resources and information visit: Passive House Accelerator